Understanding the differences between inverter and converter is crucial when powering appliances. Inverters convert DC into AC electricity, while converters convert one form of power into another, i.e., AC to DC, DC to AC, AC to AC, and even DC to DC. Because of their basic differences in functionality, their applications are varied. For example, converters are mainly usable in industrial settings, and inverters are a great choice for powering household appliances.
If you belong to the latter category, solar generators with pure-sine wave inverters fit your needs perfectly. The Jackery Solar Generator stands out in the lot with its portable design, efficiency, safety, and reliable output, irrespective of input voltage fluctuations. Depending on the battery capacity, you can power most of your appliances for hours.
Key Takeaways
- An inverter is an electrical appliance that converts direct current into alternating current for use in offices, homes, factories, and other places.
- A converter is designed to convert one form of current to another, i.e., AC to DC, DC to AC, DC to DC, and AC to AC.
- An inverter differs from a converter with respect to its functionality, type, and application.
When selecting an inverter and converter, determine your power requirements, the type of appliances to power, their efficiency, features, and size.

What is the Inverter
An inverter is a power-electronic circuit that converts direct current to alternating current. Its primary task is to allow devices using AC power to use DC power sources.
The working principle of an inverter is relatively straightforward. It takes DC power from a source and transforms it into AC power, which passes through a single dedicated outlet or a breaker panel to be distributed to multiple outlets used by appliances. The inverter continues to generate AC voltage until the DC voltage exists.

Most houses in the US use inverters as a power source to light up their offices, homes, and factories, while many use generators for the same purpose. People think both are the same, but they are actually different depending on their applications and how they operate.
When comparing inverters vs. generators, the former needs an electrical grid, while the latter converts combustible materials like gasoline and diesel into electrical energy. At the same time, both differ with respect to needed maintenance, noise, capacity, and cost.
What is the Converter
A converter, as in the name, converts or transforms one form of power into another, i.e., AC to DC and DC to AC. Think of converters as the power managers of your electrical systems that adjust the voltage to meet the power requirements of the connected devices. This conversion is required as the wrong current type and too little or too much voltage can impact your appliances and cause them to malfunction.

When dealing with AC and DC power in converters, the relationships between them depend on the type of conversion carried out. For example, an AC-DC converter (also known as a rectifier) takes the incoming AC voltage (110V) from batteries or other sources and transforms it to DC voltage (12V). It’s further distributed to charge RV’s house batteries or other appliances. Other than that, some converters transform AC to AC and DC to DC voltage.
Inverter vs. Converter
When discussing converter vs inverter, they differ in functionality, types, and applications. The differences are explained in detail:
Basics
Converters and inverters transform voltage and have different roles in electrical systems. Converters adjust the voltage levels to match the requirements of the appliances. These are versatile and can convert AC to DC, DC to AC, DC to different DC voltage levels, and AC to different voltage levels. So it’s useful for consumer electronics, industrial settings, and solar energy systems where a slight voltage variation can wreak havoc on the appliances.
On the other hand, inverters are specially designed to convert direct current to alternating current, making it usable for most household appliances. This conversion is crucial as many power sources like batteries and solar panels produce DC power, which most appliances can’t consume.
Although both devices are designed to operate efficiently, they can experience energy losses. Converters might face efficiency losses, especially if the conversion involves significant charges. Similar is the case with the inverters, where the loss is typically around 2-5%. These result from converting one form of electricity to another, impacting the overall system’s efficiency.
Types
The difference between converters and inverters is their varying nature and the types of devices they support. Converters are primarily of three types:
- AC-DC Converters: Also known as rectifiers, these converters transform an input AC power to DC power. It’s further divided into two types: diode rectifiers and phase-controlled rectifiers. The former converts an input AC voltage into a fixed DC voltage, while in the latter, a fixed AC voltage is transformed into a variable DC voltage.
- DC-DC Converters: These converters, alternatively known as choppers, convert a fixed frequency DC signal into a variable DC signal. Here, the output DC voltage may vary in amplitude from the input source voltage.
- AC-AC Converters: Similar to DC-DC converters, AC voltages of fixed frequency are converted into AC voltages of different frequencies. These are also known as cyclo-converters, and the output voltage frequency is lower than the one at the input signal.
Inverters are also of three types, which are as follows:
- Square Wave Inverter: This inverter, with four switches, a DC source, and a load, produces a square wave output. The waveform is characterized by abrupt transitions between low and high voltage levels, resulting in a series of square pulses. As a result, the quality of power produced is very low, and the square wave inverter is the cheapest.
- Modified Square Wave Inverters: As the name suggests, this type of inverter produces a square waveform, but unlike the previous type, there’s a dead space or step between the waves. It minimizes harmonics and voltage distortions, ensuring the smooth operation of electrical devices. These are more effective than square wave inverters and find application in pure loads like heaters or lamps.
- Pure Sine Wave Inverters: They are the best and most expensive inverter types. Most AC electrical appliances run on these as they have minimal voltage distortion, are predictable, and generate less electrical noise. This means you continue to get a stable voltage without any disruption.
Applications
Converters convert the power into a form that an appliance needs. Virtually all electronic appliances require converters, so a few of its typical applications are as follows:
- Consumer Electronics: Converters are installed on many household appliances used daily. For example, your laptop charger is a type of converter. It converts the high-voltage AC electricity from your wall outlet into a lower DC voltage suitable for the laptop. It potentially avoids any damage and ensures your laptop charges seamlessly.
- Industrial Applications: Converters are very handy in industrial settings. Most heavy electrical appliances in an industry demand a specific voltage and run on AC or DC power. Converters ensure the right voltage is supplied to the appliances for efficient functioning.
- Solar Energy Systems: Converters also play a crucial role in the realm of solar energy. Solar panels produce DC electricity but often need to be stored in a battery before supplying to the appliances. Here, converters adjust the voltage to match the battery’s requirements and ensure it isn’t overcharged. In certain systems, these converters regulate the DC voltage per the specific DC loads.
At the same time, a few use cases of inverters are as follows:
- Renewable Energy: Inverters are indispensable to renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power installations. The solar panels convert the sun’s rays into DC power and pass it on to the inverters, which convert it into AC power. It is then distributed to most electrical appliances for running.
- Home Appliances: In residential settings, inverters typically power household appliances during power outages. For example, the solar panels' power is converted into usable AC electricity to power televisions, refrigerators, and other household appliances. Typically, a string inverter, where a series of solar panels connect to a single inverter, makes it more efficient to manage.
- Automotive Appliances: Inverters also find their usage in the automotive industry, where they convert DC into AC power to run various electrical components. In hybrid and electric cars, the inverter converts the battery-stored DC electricity into AC to drive the motors. Due to their ability to handle heavy loads, traction inverters find their use in these systems.
Disadvantages
Despite the benefits inverters and converters offer, there are also several disadvantages. A few disadvantages of converters are:
- Poor current overload capacity
- Automatic voltage regulators are more expensive than manual ones.
At the same time, the disadvantages of inverters are as follows:
- Not ideal for motor loads
- Poor waveforms can damage sensitive appliances
- Needs a good source of power for re-charging
Here’s a table for the overall differences between an inverter and a converter:
|
Difference |
Inverter |
Converter |
|
Basic |
It transforms direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC). |
It transforms one form of electric power into another, i.e., from AC to DC and vice versa. |
|
Types |
Based on the output waveform: ● Square wave inverter ● Modified square wave inverter ● Sine wave inverter |
Based on the transformation performed: ● AC to DC converter (rectifier) ● DC to AC converter (inverter) ● DC to DC converter (chopper) ● AC to AC converter (voltage regulator) |
|
Applications |
● Renewable energy ● Home appliances ● Automotive appliances |
● Consumer electronics ● Industrial applications ● Solar energy systems |
|
Disadvantages |
● Poor waveforms damage the appliances ● Needs a good re-charging source ● Not ideal for motor loads |
● Poor current overload capacity ● Automatic voltage regulators are more expensive than manual ones. |
Which One is Suitable to Your Needs
Inverters and converters, each designed in its own way, have unique use cases and a set of advantages and disadvantages. So when choosing one, consider things like:
Power Requirements: To start, calculate your overall wattage requirements and the type of appliances you need to determine if your inverter/converter can handle the load. For example, an inverter is the right choice if you have a home to power where most of your appliances run on AC power. On the other hand, if you have both DC and AC-powered appliances, go for a converter.
Efficiency: Both an inverter and a converter incur an energy loss while transforming one power to another. But choose a high-efficiency rating to minimize the loss and power your appliances for a long time.
Features: Look for features like overload protection, low battery alert, remote monitoring, and others in many inverters and converters. These can be handy, especially when you have multiple devices to power at a time.
Size and Portability: Depending on the installation location, consider the physical size of the appliances and whether they need to be portable.
Now, similar criteria apply when deciding on inverter vs converter for RV. Your decision depends on the power sources and appliances. For instance, you won't need a converter or inverter if you have DC-powered appliances in your RV and solar panels to generate electricity.
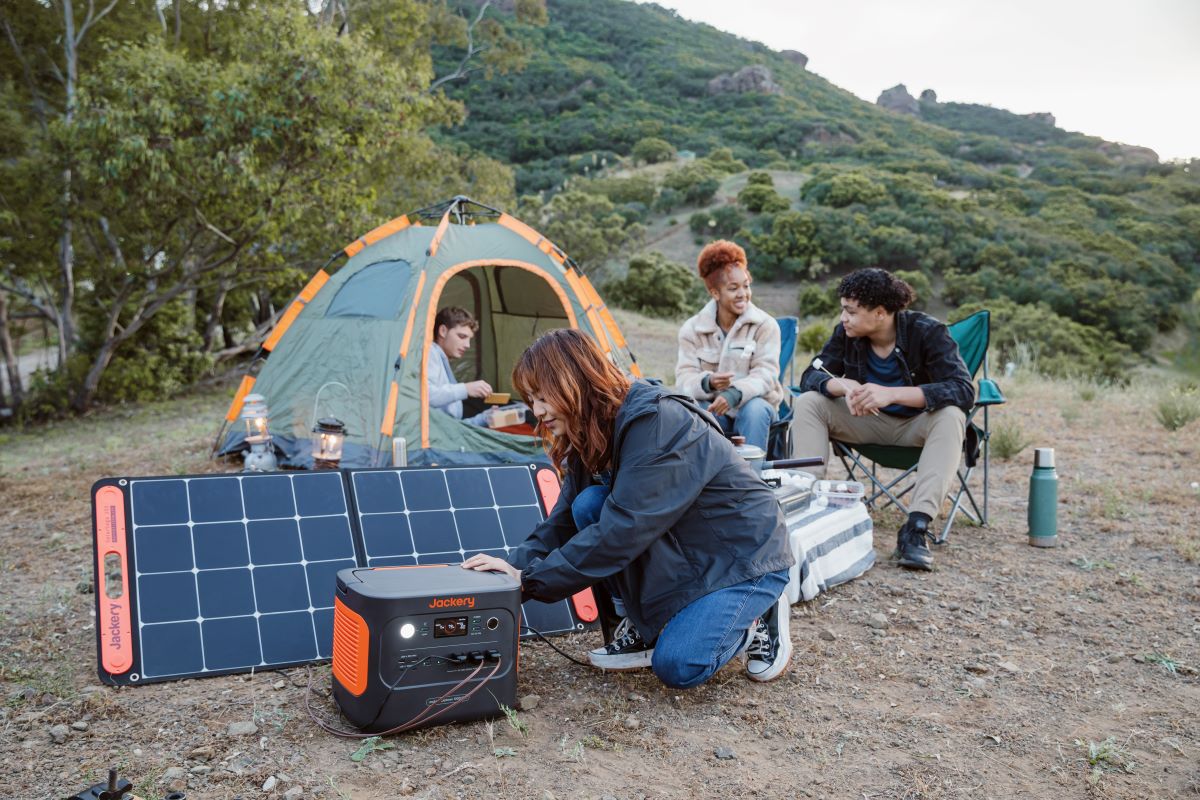
However, if you live off-grid and have AC-powered appliances to run, you need something to convert it. Inverters come as a savior and convert DC into usable AC power. You can opt for a reliable Jackery Solar Generator that boasts efficiency, little to zero power fluctuations, safety, and versatility. Besides, compared to solar panels and inverter combinations, it costs less and doesn’t take up much space in your RV.
Jackery Solar Generator Explained
A solar inverter generator is a great way to power your appliances, whether at home, living off-grid, or working. These are portable, reliable, efficient, and affordable compared to inverters and solar panels combined.
Jackery stands out in the market with its range of efficient solar generators, portable power stations, and foldable solar panels. The best part is that they come in various sizes and are suited for a number of applications.
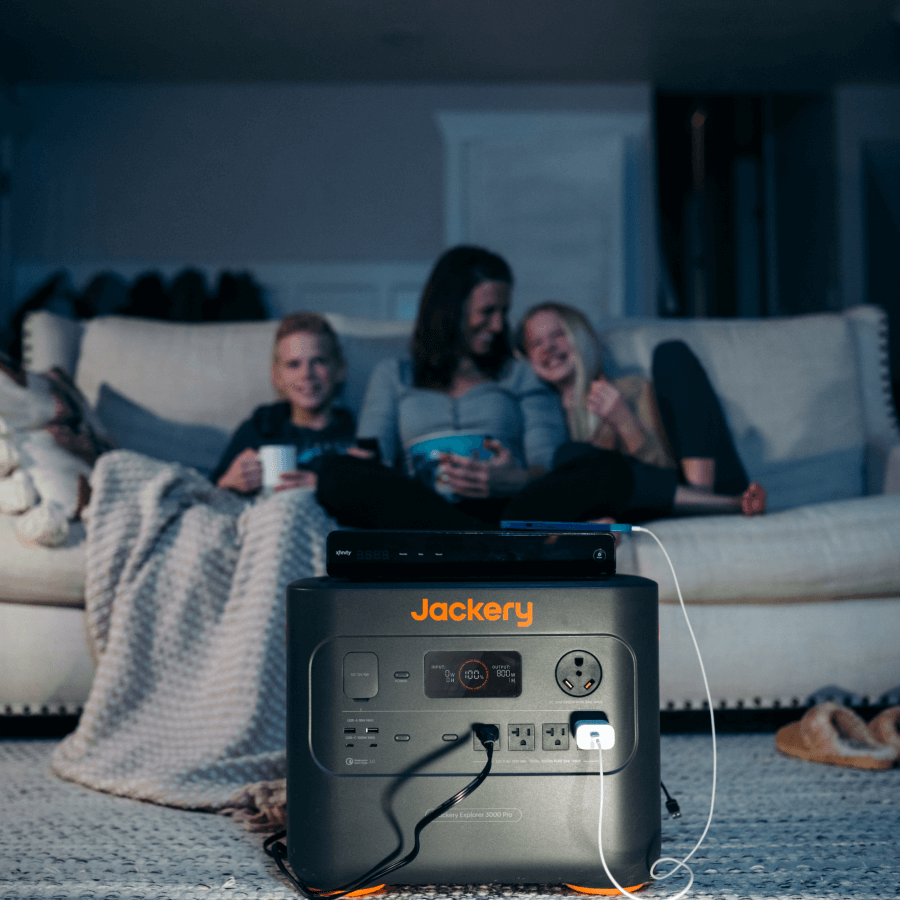
Jackery Solar Generators combine Jackery SolarSaga Solar Panels and Jackery Portable Power Stations to collect, convert, and power several appliances without failing. Its portable power station contains a pure sine-wave inverter that ensures the same output level irrespective of the voltage fluctuations in the input source. So, your appliances are safe and can run issue-free.
Jackery Solar Generator 1000 Plus
The Jackery Solar Generator 1000 Plus, with a decent battery capacity, can power up to 99% of your electrical appliances during RVing, camping, and power outages. Its foldable handle and compact design make it easy to carry around. It can support up to three add-on battery packs to expand its capability and allow you to add more appliances in the future.
Appliance Running Hours
- Portable Air Conditioner (800W): 1.3H
- Smart TVs (60W): 17.9H
- Laptop (100W): 10.7H
- Electric Cooker (900W): 1.2H
- Car Fridge (60W): 17.9H
- Ceiling Fan (75W): 14.3H

Customer Review: “I just bought a DJI FPV drone on Amazon Prime Day, and I needed a power supply that can let me fly all day. I am very satisfied with my purchase and will buy more in the future.”- Benjamin Garcia.
Jackery Solar Generator 300 Plus
If you need a portable generator capable of running multiple small appliances like cameras, drones, mobile phones, computers, speakers, and others, Jackery Solar Generator 300 Plus is a smart choice. Whether you’re spending a cozy night with your friends outside and watching a movie on a projector, camping, or powering essential household appliances, this comes in handy. And its lightweight design doesn’t take much space in your RV and is easy to carry around.
Appliance Running Hours
- Smart TVs (60W): 4.1H
- Laptop (100W): 2.4H
- Car Fridge (60W): 4.1H
- Camera (40W): 6.1H
- Ventilator (10W): 24.4H
- Drone (90W): 2.7H

Customer Review: “I purchased the Explorer 300. It will run my CPAP for 10 hours if I shut off the line heater and humidifier. If I run the humidifier, it lasts for four hours.”- Benjamin Hand.
How to Choose the Best Inverter & Converter
Whether you purchase an inverter or converter, you must ensure it fits perfectly with your needs. For that, these must fulfill a certain criterion, so let’s start with the inverters:
Identify Your Power Requirements
Identifying the power requirements of your household appliances is no rocket science. Just note down and add the running wattage of the appliances you want to power on the inverter. For example, you power a fan (70W), a LED lamp (15W), and a laptop (60W). So, your total power requirement is 70 + 15 + 60 = 145W.
Check the VA Rating
The next step is to check the VA or Volt Ampere rating of the inverter. It determines the amount of power it can deliver to its appliances. To calculate that, use the formula:
VA = Power Requirement/Power Factor
Power factor is the efficiency of an inverter, which generally stays around 0.7-0.8. So, if your power requirement is 145W, then VA= 145/0.8 = 181.25VA.
Hence, we need an inverter with a VA rating of around 200 in this case.
Get a Proper Inverter Battery
The battery is the backbone of an inverter and determines its performance and life. Now, decide how long you need the inverter to provide power or its battery capacity. It’s expressed in Ampere Hours (Ah). So, to calculate the amount of battery capacity you need, use the formula,
Battery Capacity (Ah) = Backup Time x Total Load (W)/Input Voltage (V)
So, if you need your inverter to provide at least 6 hours of backup, then
Battery Capacity (Ah) = 6 x 145/120 = 7.25Ah.
Now, if you need a converter, make sure to check into the following criteria:
Power Requirements
Similar to an inverter, it’s crucial to determine the amount of power you need at your house. Just add the running wattage of the appliances you need. So, if you run a fan (70W), an LED lamp (15W), and a laptop (60W), your overall power requirements will be 145W.
Choose the Type of Converter
The next step involves choosing the type of converter that fits your devices and their uses. Depending on their input and output, there are four types of converters: AC-DC, DC-AC, AC-AC, and DC-DC converters. AC-DC converters or rectifiers convert AC to DC power, which is handy if you have industrial appliances, medical devices, and others that run on DC electricity.
Compare the Performance
Performance evaluation is probably one of the most important factors when choosing a converter. Some of the key performance metrics include efficiency, regulation, and ripple. The higher the efficiency, the better the converter, while the less the ripple or the amount of noise produced, it’s better. Other than that, ensure the converter can maintain a constant output voltage despite fluctuating input voltage or load.
Size and Reliability
This factor is important to consider if you plan to travel with it or have limited space at your property. The smaller the size, the more portable and easy it is to carry around, and vice versa. Besides, the reliability of a converter impacts the performance and lifespan of your device. This information is found on the converters' product datasheets, ratings, or specifications.
Inverter vs. Converter FAQs
What size solar generator do I need?
The size of the generator you need depends on the type of appliances you want to power and for how long. For example, you power a portable air conditioner (800W), smart TVs (60W), and a laptop (100W) on a Jackery Solar Generator 1000 Plus.
Working Time = Capacity of Jackery Solar Generator 1000 Plus in Wh × 0.85 / Operating wattage of the appliances.
So, Working Time = 1264.64Wh × 0.85 /960W = 1.2H
Note: There’s some power loss while charging; hence, we’ve multiplied the battery capacity by 0.85.
Does my RV have an inverter or converter?
It depends. If you have DC appliances and solar panels, you won’t need anything. If you have AC-powered appliances, you need an inverter, while for any other power requirement, consider investing in a converter.
Why would you use an inverter?
Inverters convert DC electricity to AC power and are used in multiple applications, such as renewable energy, vehicle power, and household appliances.
What should you not plug into an inverter?
You shouldn’t plug any appliances powered by DC electricity into an inverter.
Should I leave my RV inverter on all the time?
It is typically recommended that you turn off your inverter when you aren’t using it. If turned on, an inverter consumes a small amount of power when it isn’t running any loads, which can deplete your batteries faster than the battery’s DC current.
Final Thoughts
In summary, understanding the inverter vs converter differences is crucial in selecting the right technology to enhance energy efficiency and meet specific power requirements. Select one depending on your needs and the efficiency of the appliances. Jackery Solar Generators is a smart investment if you have AC-powered appliances at home. These are portable, efficient, reliable, and safe and can power most appliances for hours.
Let us know in the comments if you have any doubts, like what type of solar generator, power station, or solar panels best fits your needs. Don’t forget to mention the kind of appliances you want to power so we can make the best suggestions.





































![[Add - on] Jackery Manual Transfer Switch for Explorer 5000 Plus - Jackery](http://www.jackery.com/cdn/shop/files/add-on-jackery-manual-transfer-switch-for-explorer-5000-plus-9017324.png?v=1754016782&width=170)





























































































Leave a comment